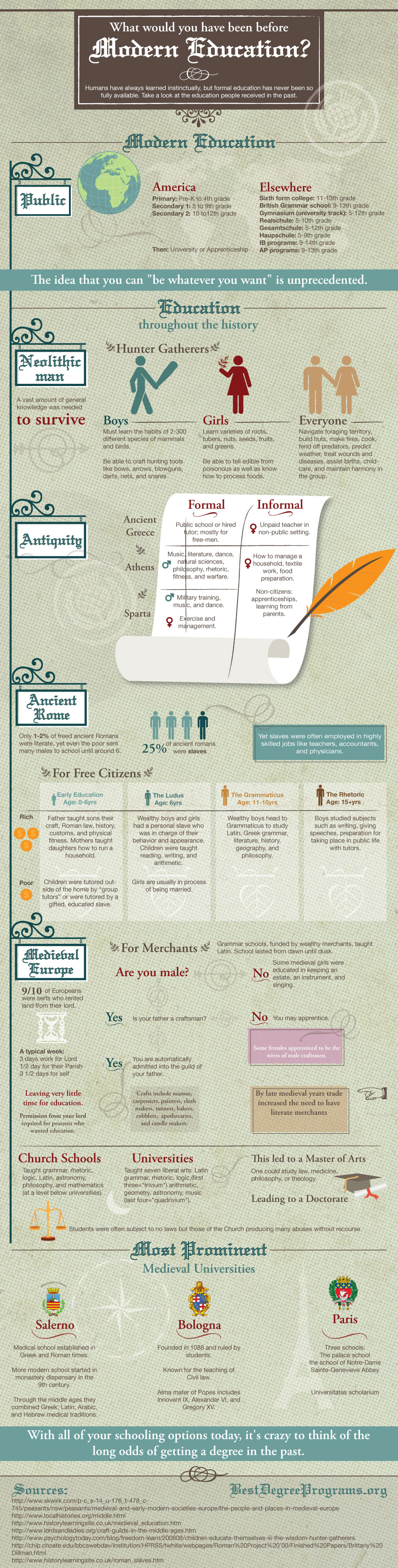
What Would You Have Been Before Modern Education?
Humans have always learned instinctively, but formal education has never been so fully available. Lets take a look at the education people received in the past.
Modern Education
Public Pre-k through Doctoral programs:
Or, close to 20 years of public education…is unprecedented in human history.
Featured Programs
America: Pre-k through 12th
(primary = pre k- 4, secondary 1 = 5-9, secondary 2 = 10-12)
Elsewhere:
Mostly the same, except–
Sixth form college (IB)
(essentially 11-13th grade)
British: grammar schools
(9-13th grade)
Gymnasium (university track)= 5-12 grades
Realschule= 5-10th grade
Gesamtschule(comprehensive school)=a mixture of college prep, vocational and remedial courses. 5-12
Haupschule=5-9 grades
IB programs (9-14th grade)
AP programs (9-13th grade)
Then–> University
Or
Apprenticeship
Drivers of knowledge:
Computers
Cloud
Internet
Projectors
E-readers
Other Tech
Massive Libraries
The idea that you can “be whatever you want” is unprecedented.
Education throughout the history of the west:
Neolithic Man[9]
Very little specialization occurred for neolithic man, however a vast amount of general knowledge was needed simply to survive.
Hunter Gatherers:
Children must learn an enormous amount to become successful adults.
Boys: must learn the habits of 2-300 different species of mammals and birds
Be able to craft hunting tools:
Bows, arrows, blowguns, darts, nets, snares.
Girls: learn many varieties of:
Roots, tubers, nuts, seeds, fruits, greens
Able to tell: edible from poisonous
Know how to process foods.
Everyone:
Navigate foraging territory
Build huts
Make fires
Cook
Fend off predators
Predict weather
Treat wounds and diseases
Assist births
Childcare
Maintain harmony in the group
Antiquity
Ancient Greece:[10]
Types of education–
Formal: public school or hired tutor; mostly for free-men (not slaves, manuel laborers, or women);
Informal: unpaid teacher in non-public setting; for women.
Athens–
Men(formal): Music, literature, dance, natural sciences, philosophy, rhetoric, fitness, warfare
Women(informal):how to manage a household, textile work, food preparation.
Non-citizens(informal): apprenticeships, learning from parents
Sparta–
Men(formal): Military training, music, dance
Women(formal): Exercise and polis management
Ancient Rome:[11]
Only 1-2% of freed ancient Romans were literate, yet even the poor sent many males to school until around 6.[12]
25% of total ancient Romans were slaves, yet[14]
Slaves were often employed in highly skilled jobs:
Teachers
Accountants
Physicians
For free citizens:
Early Education (age 0-6)–
The poor:
Father to son–their craft (carpentry, etc.), Roman law, history, customs, physical fitness
Mother to daughter–how to run a household.
The rich:
“Group-tutors” outside of the home.
Or,
Gifted, educated slave (usually Greek) tutors
The Ludus
Starting at age 6:
Wealthy boys and girls+
A personal slave (called a paedogogus) in charge of their behavior and appearance.
Taught:
Reading, writing, and arithmetic
The Grammaticus (age 11-15)
Wealthy Boys head to Grammaticus
Girls usually in process of being married
Subjects:
Latin, Greek grammar and literature, history, geography, philosophy
The Rhetoric(age 15+)
Boys studied with tutors.
Subjects: writing, giving speeches, preparation for taking place in public life.
Medieval Europe
9/10 Medieval Europeans were serfs.
Who rented land from their lord.
A typical week:
Work 3 days for Lord
1/2 day for their Parish (priests)
3 and 1/2 days for themselves
Leaving very little time for education.
Permission from your lord required for peasants who wanted education.
For merchants…
Are you male:
No: Some medieval girls were educated in keeping an estate, an instrument, and singing.
Yes:–>
Is your father a craftsman?
Yes: You are automatically admitted into the guild of your father.
No: You may apprentice.
–> In crafts such as:[5]
Masons
Carpenters
Painters
Cloth Makers
Tanners
Bakers
Cobblers
Apothecaries
Candle Makers
–>Some females apprenticed to be the wives of male craftsmen,
By late medieval years trade increased the need to have literate merchants.
Grammar schools, funded by wealthy merchants, taught Latin.
School lasted from dawn until dusk.
Classes were longer in the summer, shorter in the winter.
Dutch traders: spoke dutch but not English.
English traders: spoke English but not dutch.
Both: spoke Latin.
Church Schools
Taught Grammar, rhetoric, logic, Latin, astronomy, philosophy, mathematics
— (at a level below universities)
Universities
Seven liberal arts: Latin grammar, rhetoric, logic, arithmetic, geometry, astronomy, music.
Led to a Master of Arts.
–>
Then one could study:
Law
Medicine
Philosophy
Or theology
Leading to a Doctorate
Students:
1.) Were often subject to no laws but those of the Church.
2.) Producing many abuses without recourse.
Most prominent medieval Universities
Salerno:
Medical school established in Greek and Roman times.[6]
More modern school started in monastery dispensary in the 9th century.[7]
Through the middle ages combined:
Greek
Latin
Arabic
and Hebrew
Medical traditions.
Bologna:[8]
Founded in 1088
Ruled by students.
Known for the teaching of Civil law.
Alma mater of Popes:
Innovent IX
Alexander VI
and Gregory XV
Paris:
Three schools:
The palace school
The school of Notre-Dame
Sainte-Genevieve Abbey
Universitatas scholarium
————
With all of your schooling options today, it’s crazy to think of the long odds of getting a degree in the past.
Citations:
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Education_in_Germany
- http://www.skwirk.com/p-c_s-14_u-176_t-478_c-1745/peasants/nsw/peasants/medieval-and-early-modern-societies-europe/the-people-and-places-in-medieval-europe
- http://www.localhistories.org/middle.html
- http://www.historylearningsite.co.uk/medieval_education.htm
- http://www.lordsandladies.org/craft-guilds-in-the-middle-ages.htm
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/University_of_Salerno
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Schola_Medica_Salernitana
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/University_of_Bologna
- http://www.psychologytoday.com/blog/freedom-learn/200808/children-educate-themselves-iii-the-wisdom-hunter-gatherers
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Education_in_ancient_Greece
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/History_of_education#Greece_and_Rome
- http://www.historylearningsite.co.uk/roman_slaves.htm